Conventional Tomography Uses Which of the Following Principles
During conventional tomography the image receptor. Positron emission tomography PET a type of radionuclide scanning Radionuclide Scanning Radionuclide scanning uses the radiation released by radionuclides called nuclear decay to produce images.

Low Dose Contrast Ct For Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Assessment Results From The Prospective Spectacular Study Spectral Ct Assessment Prior To Tavr Journal Of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography
Which of the following finds application in bone mineral assay for evaluation of osteoporosis.

. To the computer for processing. Linear tomography is divided further into two types. A computer is used to reconstruct images of sectional anatomy.
Out of plane tissue are blurred D. Reduces radiographic contrast resolution. CT may be done with or without IV contrast.
Common uses of conventional angiography include the following. Typically it is the first imaging method indicated to evaluate the extremities chest and sometimes the spine and abdomen. Is focused to the automatic plane of interest.
Compared to projection radiography conventional tomography results in improved contrast resolution because A. These areas contain important structures with densities that differ from those of adjacent tissues. Moves opposite the x-ray tube in a seesaw motion.
CT is the most accurate study for detecting and localizing urinary calculi. A useful analogy is to regard the technique as one that enables the patient to be imaged in slices like a loaf of sliced bread see Fig. Moves with the x-ray tube similarly to the x-ray tube tower assembly in fluoroscopy.
Conventional tomography employs what principle. Linear tomography tomography in which the tube and film move in the same direction. These areas contain important structures with densities that differ from those of adjacent tissues.
Radiography is the most readily available imaging method. When the planigraphic principle is used to alter the focal plane the fulcrum system is _____. Acquiring information from the patient by using special motions of the X-ray tube and detectors.
Study Tomography 1 flashcards from Thomas Couchs class online or in Brainscapes iPhone or Android app. The limitations of conventional tomography include all of the following except. To detect acute hemorrhage in the brain urinary calculi and lung nodules.
The goal of CT is to overcome the limitations of radiography and tomography by achieving the following. A computer is used to calculate radiation dose to the patient. The technique for axial tomography was developed by.
Tap again to see term. Narrow angle tomography a type of tomography that results in thicker sections for examination. Radiography is the most readily available imaging method.
Coronary angiography is usually done before percutaneous or surgical interventions involving the coronary arteries or heart valves. Uses of Conventional Radiography. For virtual CT colonoscopy CT colonography oral contrast is given and air is introduced into the rectum via a flexible thin-diameter rubber catheter.
Precise beam collimation is employed C. Is focused by the angle of movement. Pluridirectional tomography tomography in which there is.
Noncontrast CT is used. Click card to see definition. The presence of ghost images on the film.
During conventional Tomography structures lying outside the object plane are blurred because of what. Conventional tomography is now less commonly used because of the availability of cross-sectional imaging techniques such as US CT and MRI. The x-ray beam is selectively filtered B.
A radionuclide is an unstable isotope that becomes more stable by releasing energy. Conventional tomography is a specialized radiographic technique developed originally for producing radiographs that showed only a section or slice of a patient. To characterize bone fractures and other skeletal abnormalities.
The _____ is raised or lowered while the _____ remains stationary. Basic Principle of Tomography. IV contrast is used.
There are 2 basic types of tomography. CT colonoscopy produces high-resolution 3-dimensional images of the colon that closely simulate the detail and appearance of optical. Each individual tomographic image or slice shows the.
Then thin-section CT of the entire colon is done. The computer uses special mathematical techniques to reconstruct the CT image in a finite number of steps called image reconstruction algorithms. Tomography is an x-ray technique in which shadows of superimposed structures are blurred out by a moving x-ray tube.
It is usually done with cardiac catheterization. The term computed tomography or CT refers to a computerized x-ray imaging procedure in which a narrow beam of x-rays is aimed at a patient and quickly rotated around the body producing signals that are processed by the machines computer to generate cross-sectional imagesor slicesof the body. These slices are called.
Read more uses compounds containing radionuclides that decay by releasing a. Typically it is the first imaging method indicated to evaluate the extremities chest and sometimes the spine and abdomen. Click again to see term.
The principle advantage of CT imaging over other x-ray imaging is. Uses of Conventional Radiography. Tap card to see definition.
If there is synchronous movement bw either of two among the three that is the patient the x-ray tube or the image receptor than there is blurring of image causes While movement only one thing is constant that is the fulcrum point of the tomographic equipment and the plane which posses this point is well demonstrated. Learn faster with spaced repetition.
What Is The Difference Between An X Ray A Ct Scan And An Mri

Dual Energy Computed Tomography Radiologic Clinics

Computed Tomography Of The Head An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

X Ray Computed Tomography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Safe And Effective Use Of Cone Beam Computed Tomography
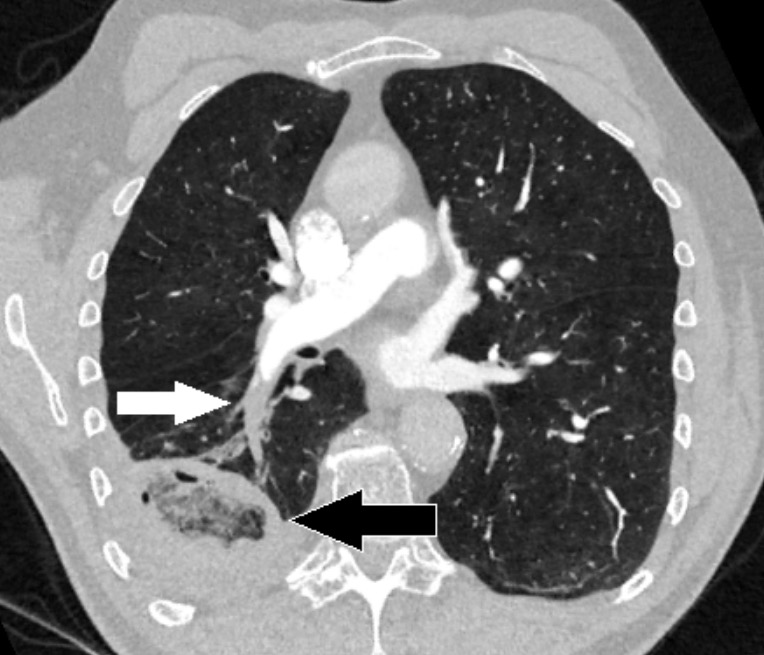
Computed Tomography Ct Concise Medical Knowledge

Dual Energy Ct Images Pearls And Pitfalls Radiographics

Practical Applications Of Dual Energy Computed Tomography In The Acute Abdomen Radiologic Clinics

Customised Weight Based Volume Contrast Media Protocol In Ct Of Chest Abdomen And Pelvis Examination Journal Of Medical Imaging And Radiation Sciences

Linear Tomography Technology Britannica

Dual Energy Computed Tomography Radiologic Clinics

Normal Kidneys On 4 Phase Ct Study Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Radiology Study Case

Pearls Pitfalls And Problems In Dual Energy Computed Tomography Imaging Of The Body Radiologic Clinics

Computed Tomography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Computed Tomography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Computed Tomography Ct Or Cat Scan Of The Bones Johns Hopkins Medicine

The Reveal Device Is An Implantable Loop Recorder Device That Wirelessly Records The Cardiac Rhythm It Is Different Medical Mnemonics Cardiac Rhythms Medical

The Role Of Dual Energy Computed Tomography In Assessment Of Abdominal Oncology And Beyond Radiologic Clinics

Comments
Post a Comment